Immersive Learning & Retention
Harnessing virtual reality for learning and development – Business Use Cases
Maximise performance while minimising risk with Virtual Reality training.
When sight and sound are combined with movement, learners develop conditioned responses, problem-solving skills, and muscle memory – even before they’re on the job.
- Create neural pathways to build new habits
- Develop motor responses based on audio/visual cues and environmental signals
- Safely expose learners to a variety of scenarios with repetition, practice, and feedback
Try CenarioVR today. It’s the tool you need to maximise learning performance and outcomes.
VR Business Use Cases & Results
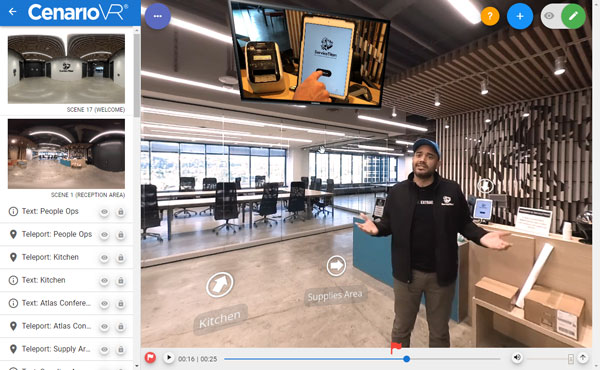
Employee On boarding & Induction
Service Titan Corporation – Uses CenarioVR to onboard staff at their headquarters. New employees are introduced to the facility and to key staff through VR to encourage them to discover all that is offered at the facility, including processes, workplace safety features and more.

Honeygrow – This Philadelphia-based restaurant chain, reported that within 30 days of implementing VR training for employee onboarding, the number of team members fully-certified on culture and training soared from 50% to 77%.

ASADA – found that by using virtual reality to educate athletes about the doping control process it gave learners greater control as opposed to learning with videos and/or infographics. This increased the confidence of athletes when approached with this intimidating process.


Image from: UNSW
WH&S/Compliance Training

Australia’s UNSW School of Mining Engineering – Uses VR to simulate an escape from a potentially fatal outburst event in a mine, allowing students to practice responding to a hazardous situation in an immersive simulated terrain.
Sales & Customer Service Training
Walmart – Proved that Virtual Reality solves sales skills training at scale. Walmart rolled out a national Black Friday sales training program for 1 million employees across 5,000 stores in the US. VR enabled sales staff to make in-the-moment decisions – from customer service needs to safety.
“VR gives us a practical, scalable way to teach new skills, give associates more confidence in their jobs and make work more exciting and fun.”
Brock McKeel, Senior Director, Central Operations, Walmart

Image from: Walmart
Lowe’s – More than 400 employees have been trained using VR, with 90% reporting that VR training helps them better serve customers.
TechRadar – Google tested two groups in how to use an espresso machine: One with YouTube videos, and one with VR. The VR team not only learned quicker, but also made fewer mistakes, and took less time to operate the machinery.
Chick-Fil-A – This US-based fast food chain uses CenarioVR to train front line workers on their customer service skills. Immersive training allows front-line employees to experience and navigate difficult interactions in a consequence-free environment. The increased repetition enabled by VR creates confidence and comfort when employees are faced with a difficult situation in the actual working environment.
Verizon – As a retailer with 1,600 stores in the US, selling high-end electronics items, such as the hottest smartphone tech, Verizon was aware that their retail locations could be a target for thieves. The company initiated a VR program that trains their retail employees how to respond in the event of a robbery. According to Chief Security Officer Michael Mason, the objective isn’t to protect inventory, it’s to protect employees. The value is in training employees on facing extremely dangerous situations without real-world consequences.
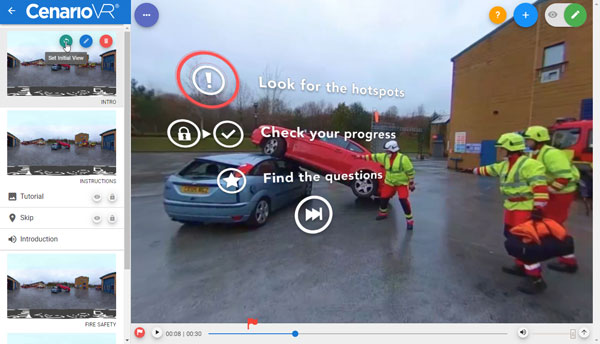
Emergency Services & High Risk
South Wales Fire & Rescue – Training firefighters on extricating a casualty from a major road accident, simulating a real life-or-death scenario where decisions need to be made in a high-stress environment.
Tucson Sheriff’s Department – Pima County created a VR training module used to simulate a variety of scenarios ranging from a suspicious man in a parking lot, to burglary in a factory, to more hostile situations. A mistake during simulation could lead to a tragic situation for the bystander, victim or officer, and the goal is to avoid such a situation in reality.

More on YouTube: Vocativ
Military

US Navy – In the first two months after the US Navy began using VR for recruiting, leads of potential recruits have more than doubled compared to the previous two years combined.
Interpersonal Skills & Empathy
Dementia Australia – Launched a VR smartphone app for carers and staff so that they could experience living with dementia, with the objective of increasing empathy and providing better care.
Hilton Hotels – Is using VR to help its corporate employees experience what it’s like to work in a hotel so that they understand how their decisions affect hotel employees.
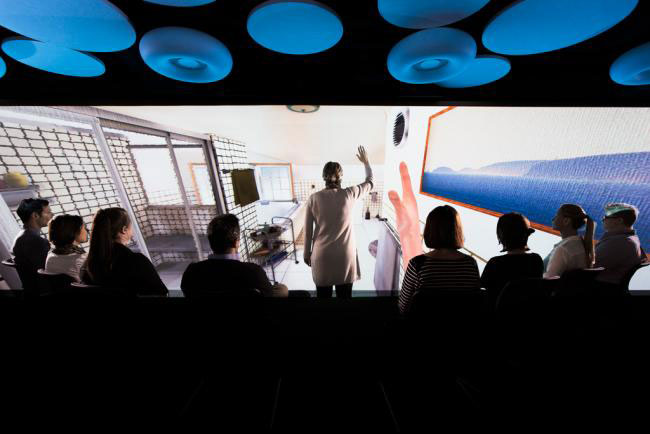

Image From: Dementia Australia

Real Estate

Domain – Visualisation and walk-throughs of existing or yet-to-be-built buildings, units and homes, enables customers to experience the property from every aspect and provides a sense of space and level of detail never experienced through conventional marketing.
Manufacturing & Procedural
UPS – Replaced their driving simulation warehouses, which were expensive to operate, with VR.
AIB International – Uses CenarioVR to train line inspectors to identify food safety procedures through a plant floor inspection. A single mistake in any process on the line can result in a complete loss of production, so ensuring that each employee has experienced the process before live production is vital.

Image from: UPS
American Airlines – Initiated a simulated VR training program aimed at the 2,000 new flight attendants each year. The training was aimed at reformulating the entire hiring process. Visualising the cabin through previous training modules proved difficult. VR allows learners to interact within the environment, locate emergency equipment in real time and familiarise themselves with all tasks before practicing them in a flight simulator or in a real aircraft.
Boeing – Boeing is using VR for certain more specialised manufacturing tasks. Some jobs are more ‘tribal’, such as working with a cargo door seal, which goes across the joint of the fuselage. It is a process that takes 50 individual steps and there’s only a handful of people that know how to do this in the company. If someone is sick or on vacation, there are delays. Boeing estimates they can cut training time by 75% per person through VR training.
Ford – Used VR to assess the physical labor that’s needed to build a vehicle, ensure the manufacturing process is feasible, and identify areas which may cause fatigue, strain and injury.

Image from: Stanford University
Hospitals
Stanford University – Found that VR imaging gives radiologists more confidence when diagnosing an issue and specialists more conviction when heading into difficult procedures.
Miami Children’s Health System – VR training scenarios included starting an IV or catheter, cardiopulmonary resuscitation and nasal-gastric tube insertion. CEO Dr Narendra Kini reported that the retention level remained at 80% one whole year after VR training, compared with 20% after only one week.
Research: Annals of Surgery (Seattle WA) – Randomised, double-blind study surgical simulation VR training for gallbladder dissection. VR was tested vs conventional teaching for training surgical residents, and it was found that the VR group was 29% faster and were 6 times less likely to cause an error in the procedure.
Research (Source: Fortune) – VR reduces costs: 65,000 elderly care facilities in America currently spend on average $3,000 per employee to learn tracheal insertion. Current VR software is being developed for tracheal insertion training, at a cost of $40 per person.